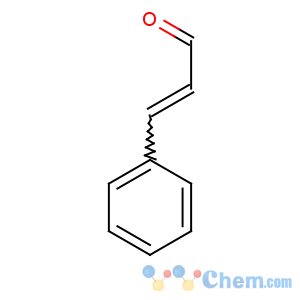
Title: Cinnamaldehyde
CAS Registry Number: 104-55-2
CAS Name: 3-Phenyl-2-propenal
Synonyms: cinnamic aldehyde; phenylacrolein; cinnamal
Molecular Formula: C9H8O
Molecular Weight: 132.16
Percent Composition: C 81.79%, H 6.10%, O 12.11%
Literature References: Found in Ceylon and Chinese cinnamon oils as the
trans-form. Prepn by condensation of benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde: Peine,
Ber. 17, 2117 (1884);
JP 163097 (1944 to Ogawa Chem. Ind.); from 2-chloroallylbenzene: Bert, Dorier,
Compt. Rend. 191, 332 (1930); Bert, Annequin,
ibid. 192, 1315 (1931); by condensation of styrene with formylmethylaniline:
GB 504125 (1939 to I. G. Farben); by oxidation of cinnamyl alc: Holum,
J. Org. Chem. 26, 4814 (1961); Traynelis, Hergenrother,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86, 298 (1964). Isoln from woodrotting fungus,
Stereum subpileatum Berk. & Curt.: Birkinshaw
et al., Biochem. J. 66, 188 (1957). Toxicity data: P. M. Jenner
et al., Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 2, 327 (1964). Review of risk assessment as fragrance ingredient: D. Bickers
et al., Food Chem. Toxicol. 43, 799-836 (2005); of toxicology: J. Cocchiara
et al., ibid. 867-923.
Properties: Yellowish oily liquid, strong odor of cinnamon. d2525 1.048-1.052. Volatile with steam. mp -7.5°. bp1.0 76.1°; bp5 105.8°; bp10 120.0°; bp20 135.7°; bp40 152.2°; bp60 163.7°; bp100 177.7°; bp200 199.3°; bp400 222.4°; bp760 246.0° (some dec).
nD20 1.618-1.623. Flash point, closed cup: >100°C. Dissolves in about 700 parts water, in about 7 vols of 60% alc. Misc with alcohol, ether, chloroform, oils. LD50 in rats (mg/kg): 2220 orally (Jenner).
Melting point: mp -7.5°
Boiling point: bp1.0 76.1°; bp5 105.8°; bp10 120.0°; bp20 135.7°; bp40 152.2°; bp60 163.7°; bp100 177.7°; bp200 199.3°; bp400 222.4°; bp760 246.0° (some dec)
Flash point: Flash point, closed cup: >100°C
Index of refraction: nD20 1.618-1.623
Density: d2525 1.048-1.052
Toxicity data: LD50 in rats (mg/kg): 2220 orally (Jenner)
Use: In the flavor and perfume industry.