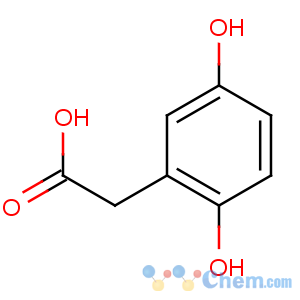
Title: Homogentisic Acid
CAS Registry Number: 451-13-8
CAS Name: 2,5-Dihydroxybenzeneacetic acid
Synonyms: 2,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid; 2,5-dihydroxy-a-toluic acid
Molecular Formula: C8H8O4
Molecular Weight: 168.15
Percent Composition: C 57.14%, H 4.80%, O 38.06%
Literature References: An important intermediate in metabolism of tyrosine and phenylalanine,
q.q.v.. Occurs in plants and in the urine of alkaptonurics: Garrod,
Inborn Errors of Metabolism (Oxford Medical Publications, London, 1923, and later). Isoln from alkaptonuric urine: M?rner,
Z. Physiol. Chem. 117, 85 (1921). Synthesis from 2,5-dihydroxymandelic acid or from 2,5-dihydroxyphenylglyoxylic acid by boiling with fuming HI: Neubauer, Flatow,
ibid. 52, 395 (1907). Alternate syntheses: L. DeForrest Abbott, J. D. Smith,
J. Biol. Chem. 179, 365 (1949); S. B. Bostock, A. H. Renfrew,
Synthesis 1978, 66; J. L. Bloomer, K. M. Damodaran,
ibid. 1980, 111. Biosynthesis from tyrosine: Davies
et al., J. Chem. Soc. 1964, 3126. Metabolic studies: W. E. Knox, M. LeMay-Knox,
Biochem. J. 49, 686 (1951); B. N. LaDu, V. G. Zannoni,
J. Biol. Chem. 217, 777 (1955).
Derivative Type: Monohydrate
Properties: Prisms from water. Anhydrous leaflets from hot alcohol + chloroform, mp 152°. Freely sol in water, alcohol, ether; insol in chloroform, benzene. Easily dehydrated to the lactone. Aq solns are stable.
Melting point: mp 152°
Derivative Type: Dimethyl ether
Molecular Formula: C10H12O4
Molecular Weight: 196.20
Percent Composition: C 61.22%, H 6.16%, O 32.62%
Properties: mp 124.5°.
Melting point: mp 124.5°
Derivative Type: Methyl ester dimethyl ether
Molecular Formula: C11H14O4
Molecular Weight: 210.23
Percent Composition: C 62.84%, H 6.71%, O 30.44%
Properties: mp 45°.
Melting point: mp 45°