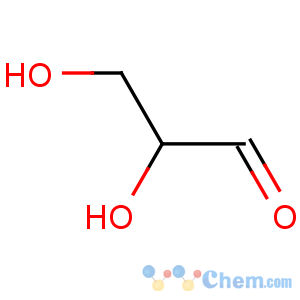
Title: Glyceraldehyde
CAS Registry Number: 56-82-6
CAS Name: 2,3-Dihydroxypropanal
Synonyms: DL-glyceraldehyde; glyceric aldehyde; a,b-dihydroxypropionaldehyde
Molecular Formula: C3H6O3
Molecular Weight: 90.08
Percent Composition: C 40.00%, H 6.71%, O 53.28%
Literature References: Obtained with its isomer dihydroxyacetone from glycerol by mild oxidation: Witzemann,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 36, 2227 (1914).
See also Org. Synth. coll. vol. II, 305 (1943). The equilibrium mixture of glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone is called
glycerose. The two isomers are convertible into another through a common enediol resulting from the migration of hydrogen atoms (Lobry de Bruyn-van Eckenstein rearrangement). The equilibrium mixture plays an important role in the fermentation of sugars and in the biogenesis of constituents of the animal organism,
cf. L.F. Fieser, M. Fieser,
Advanced Organic Chemistry (Reinhold, New York, 1961) pp 78, 284, 405. Glyceraldehyde is the simplest aldose; the D- and L-forms are the configurational reference standard for carbohydrates. The two forms have been obtained through the action of nitrous acid on the corresponding form of 3-amino-2-hydroxypropanal: Wohl, Momber,
Ber. 47, 3346 (1914); Pictet, Barbier,
Helv. Chim. Acta 4, 924 (1921);
cf. Baer, Fischer,
Science 88, 108 (1938). Prepn of L-glyceraldehyde from L-sorbose and of D-glyceraldehyde from D-fructose: Perlin,
Methods Carbohydr. Chem. 1, 61 (1962).
Properties: Tasteless crystals from alcohol + ether, d1818 1.455. mp 145°. Distills at 140-150° (bath temp) and 0.8 mm pressure. 100 ml water dissolve 3 g at 18°. Insol in benzene, petr ether, pentane. Osazone, mp 132°.
Melting point: mp 145°; mp 132°
Density: d1818 1.455
Derivative Type: L-Form
CAS Registry Number: 497-09-6
Synonyms: (
S)-(-)-2,3-Dihydroxypropanol
Properties: [a]D25 -8.7° (c = 2 in H2O). Its dimethylacetal, bp17-20 126-129°. [a]D26 -20.9° (p = 9.22).
Boiling point: bp17-20 126-129°
Optical Rotation: [a]D25 -8.7° (c = 2 in H2O); [a]D26 -20.9° (p = 9.22)
Derivative Type: D-Form
CAS Registry Number: 453-17-8
Properties: [a]D25 +8.7° (c = 2 in H2O). Its dimethylacetal, bp17 127-129°, bp10 123-126°. [a]D15 +21.2° (c = 18).
Boiling point: bp17 127-129°; bp10 123-126°
Optical Rotation: [a]D25 +8.7° (c = 2 in H2O); [a]D15 +21.2° (c = 18)