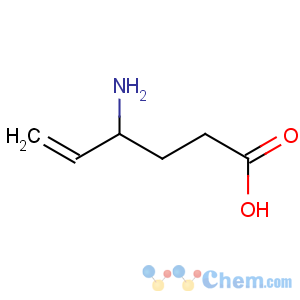
Title: Vigabatrin
CAS Registry Number: 60643-86-9
CAS Name: 4-Amino-5-hexenoic acid
Synonyms: g-vinyl-g-aminobutyric acid; gamma-vinyl GABA; g-vinyl GABA; GVG
Manufacturers' Codes: MDL-71754; RMI-71754
Trademarks: Sabril (HMR)
Molecular Formula: C6H11NO2
Molecular Weight: 129.16
Percent Composition: C 55.79%, H 8.58%, N 10.84%, O 24.77%
Literature References: Irreversible inhibitor of g-aminobutyric acid transaminase, the enzyme responsible for the degradation of the neurotransmitter g-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Prepn: B. W. Metcalf, M. Jung,
US 3960927 (1976 to Richardson-Merrell); and
in vitro enzyme inactivation: B. Lippert
et al., Eur. J. Biochem. 74, 441 (1977). Mechanism of action study: P. J. Schechter
et al., Eur. J. Pharmacol. 45, 319 (1977). Anticonvulsant activity and toxicity studies: W. L?scher,
Neuropharmacology 21, 803 (1982). HPLC determn in plasma and urine: J. A. Smithers
et al., J. Chromatogr. 341, 232 (1985). The
S(+)-enantiomer is the pharmacologically active form. Pharmacokinetics of enantiomers in humans: K. D. Haegele, P. J. Schechter,
Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 40, 581 (1986). Clinical studies in treatment resistant epilepsy: C. A. Tassinari
et al., Arch. Neurol. 44, 907 (1987); T. R. Browne
et al., Neurology 37, 184 (1987). Series of articles on clinical use in adult and childhood epilepsy:
J. Child Neurol. 6, Suppl. 2, S3-S69 (1991). Reviews of early literature and mechanism of action: M. J. Iadarola, K. Gale,
Mol. Cell. Biochem. 39, 305-330 (1981); of pharmacology and toxicology: E. J. Hammond, B. J. Wilder,
Clin. Neuropharmacol. 8, 1-12 (1985).
Review: S. M. Grant, R. C. Heel,
Drugs 41, 889-926 (1991).
Properties: Crystals from acetone/water, mp 209°. Freely sol in water. LD50 i.p. in mice: >2500 mg/kg (L?scher).
Melting point: mp 209°
Toxicity data: LD50 i.p. in mice: >2500 mg/kg (L?scher)
Therap-Cat: Anticonvulsant.
Keywords: Anticonvulsant.