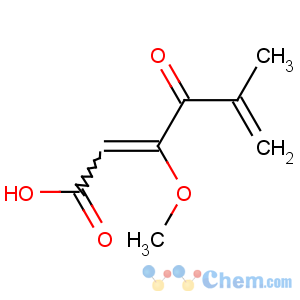
Title: Penicillic Acid
CAS Registry Number: 90-65-3
CAS Name: 3-Methoxy-5-methyl-4-oxo-2,5-hexadienoic acid
Synonyms: g-keto-b-methoxy-d-methylene-Da-hexenoic acid
Molecular Formula: C8H10O4
Molecular Weight: 170.16
Percent Composition: C 56.47%, H 5.92%, O 37.61%
Literature References: Antibiotic mycotoxin produced by the following fungi:
Penicillium puberulum, P. cyclopium, P. thomii, P. suaveolens, P. baarnense, Aspergillus ochraceus, A. melleus. Isoln: Alsberg, Black,
USDA Bur. Plant Ind. Bull. 270, (1913); Birkinshaw
et al., Biochem. J. 30, 394 (1936); Oxford
et al., Chem. Ind. (London) 20, 22 (1942); Karow
et al., Arch. Biochem. 5, 279 (1944); Burton,
Nature 165, 274 (1950); Natori
et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull. 18, 2259 (1970). Activity studies: Suzuki
et al., Agric. Biol. Chem. 35, 287 (1971). Acid in tautomeric equilibrium with its lactone. Structure: Birkinshaw
et al., loc. cit. Physical properties: Kovac, Solcaniova,
Tetrahedron 25, 3617 (1969). Synthesis: Raphael,
Nature 160, 261 (1947);
J. Chem. Soc. 1948, 1508; C. L. Yeh
et al., Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 3987. Biosynthesis: Birch
et al., J. Chem. Soc. 1958, 4582; Bentley, Keil,
J. Biol. Chem. 237, 867 (1962). Physicochemical data: A. E. Pohland
et al., Pure Appl. Chem. 54, 2219 (1982). Toxicity studies: P. K. Chan
et al., Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 52, 1 (1980); P. K. Chan, A. W. Hayes,
J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 7, 169 (1981). Evaluation of carcinogenic risk:
IARC Monographs 10, 211-216 (1976).
Review: Ciegler
et al., "Patulin, Penicillic Acid and Other Carcinogenic Lactones" in
Microbial Toxins vol. VI, A. Ciegler
et al., Eds. (Academic Press, New York, 1971) p 414.
Properties: Needles from petr ether, mp 83-84°. uv max: about 220 nm. Acid reaction, turns Congo red paper blue. Moderately sol in cold water (2 g/100 ml); freely sol in hot water, alcohol, ether, benzene, chloroform; slightly sol in hot petr ether. Practically insol in pentane-hexane. LD50 i.p. in mice: 90.00 mg/kg (Chan
et al.).
Melting point: mp 83-84°
Absorption maximum: uv max: about 220 nm
Toxicity data: LD50 i.p. in mice: 90.00 mg/kg (Chan
et al.)
Derivative Type: Monohydrate
Properties: Large transparent monoclinic or triclinic, rhombic crystals from water, mp 58-64°.
Melting point: mp 58-64°