You are here:
HomeProductsLidocaine Local Anesthetic Drugs Lidocaine Hydrochloride for Pure Topical
Lidocaine Local Anesthetic Drugs Lidocaine Hydrochloride for Pure Topical
-
- Product NameLidocaine Local Anesthetic Drugs Lidocaine Hydrochloride for Pure Topical
- CAS No.73-78-9
- Purity99%
- Min Quantity80000Kilograms
- Price100~700

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
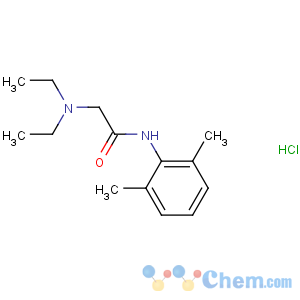
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Lidocaine Local Anesthetic Drugs Lidocaine Hydrochloride for Pure Topical
Product Details:
Product name: Lidocaine Hydrochloride
Other name: Lidocaine HCL, Lidocaine, Lidocaine Base
Cas: 73-78-9
MF: C14H23ClN2O
MW: 270.7982
Melting point: 350.8° C at 760 mmHg
Usage: Local anesthetics, antiarrhythmic drugs, used for a variety of anesthesia and rapid ventricular arrhythmia
Description:
Lidocaine may be absorbed following topical administration to mucous membranes, its rate and extent of absorption depending upon concentration and total dose administered, the specific site of application, and duration of exposure. In general, the rate of absorption of local anesthetic agents following topical application occurs most rapidly after intratracheal administration. Lidocaine is also well-absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, but little intact drug may appear in the circulation because of biotransformation in the liver.
Lidocaine is metabolized rapidly by the liver, and metabolites and unchanged drug are excreted by the kidneys. Biotransformation includes oxidative N-dealkylation, ring hydroxylation, cleavage of the amide linkage, and conjugation. N-dealkylation, a major pathway of biotransformation, yields the metabolites monoethylglycinexylidide and glycinexylidide.
The plasma binding of lidocaine is dependent on drug concentration, and the fraction bound decreases with increasing concentration. At concentrations of 1 to 4 mcg of free base per mL, 60 to 80 percent of lidocaine is protein bound. Binding is also dependent on the plasma concentration of the alpha-1-acid glycoprotein.

- Lidocaine Local Anesthetic Drugs Lidocaine Hydrochloride for Pure Topical




