2-Ketoglutaric acid
-
- Product Name2-Ketoglutaric acid
- CAS No.328-50-7
- Purity
- Min Quantity
- Price~

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
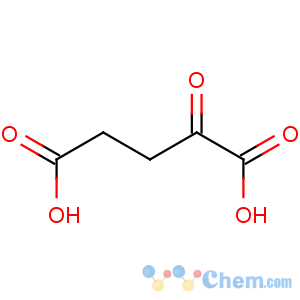 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure

- 2-Ketoglutaric acid
Detailed Description
Synonyms: 2-KETOGLUTARIC ACID;2-OXOGLUTARIC ACID;2-OXOPENTANEDIOIC ACID;A-KETOGLUTARIC ACID;ALPHA-KETOGLUTARIC ACID;GAMMA-KETOGLUTARIC ACID;FEMA 3891;KETO-GLUProduct Details:
Place of Origin: China
Certification: ISO9001
Brand:YuanCheng
Payment & Shipping Terms:
Minimum Order Quantity:1kg
Supply Ability:500kg/month
Delivery Time:within 24 hours after payment
Payment Terms:Western Union, MoneyGram, T/T
Package:25kg/cardboad drum
Appearance:White to off white crystalline powder
Product Description:
CAS: 328-50-7
MF: C5H6O5
MW: 146.1
EINECS:206-330-3
Purity:99%
mp 113-115 °C
FEMA 3891
Functions:
Krebs cycle
α-Ketoglutarate is a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle, coming after isocitrate and before succinyl CoA. Anaplerotic reactions can replenish the cycle at this juncture by synthesizing α-ketoglutarate from transamination of glutamate, or through action of glutamate dehydrogenase on glutamate.
Formation of amino acids
Glutamine is synthesized from glutamate by glutamine synthetase, which utilizes an ATP to form glutamyl phosphate; this intermediate is attacked by ammonia as a nucleophile giving glutamine and inorganic phosphate.
Nitrogen transporter
Another function is to combine with nitrogen released in the cell, therefore preventing nitrogen overload.
α-Ketoglutarate is one of the most important nitrogen transporters in metabolic pathways. The amino groups of amino acids are attached to it (by transamination) and carried to the liver where the urea cycle takes place.
α-Ketoglutarate is transaminated, along with glutamine, to form the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate. Glutamate can then be decarboxylated (requiring vitamin B6) into the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA.
It is reported that high ammonia and/or high nitrogen levels may occur with high protein intake, excessive aluminum exposure, Reye's syndrome, cirrhosis, and urea cycle disorder.
It plays a role in detoxification of ammonia in brain
Relationship to molecular oxygen
Acting as a co-substrate, it also plays important function in oxidation reactions involving molecular oxygen.
Molecular oxygen (O2) directly oxidizes many compounds to produce useful products in an organism, such as antibiotics, etc., in reactions catalyzed by oxygenases. In many oxygenases, α-ketoglutarate helps the reaction by being oxidized together with the main substrate. In fact, one of the α-ketoglutarate-dependent oxygenases is an O2 sensor, informing the organism the oxygen level in its environment.
In combination with molecular oxygen, alpha-ketoglutarate is one of the requirements for the hydroxylation of proline to hydroxyproline in the production of Type 1 Collagen.
Dietary supplement
α-Ketoglutaric acids is sold as a dietary supplement and to body builders as AKG or a-KG with the claim that it improves peak athletic performance. This claim is based on studies that show excess ammonia in the body can combine with alpha-ketoglutarate, reducing problems associated with ammonia toxicity.However, the only studies that show alpha-ketoglutarate can reduce ammonia toxicity have been performed in hemodialysis patients.
Longevity
A study released on May 14, 2014 links α-ketoglutarate with significantly increased lifespan in nematode worms. Its anion, α-ketoglutarate (α-KG, also called oxo-glutarate) is an important biological compound. It is the keto acid produced by deamination of glutamate, and is an intermediate in the Krebs cycle.